White Matter Tracts
The white matter tracts of cerebrum can be categorized into three major groups, including commissural pathways, association pathways, and projection pathwas.
Commissural pathways are white matter tracts that connect corresponding regions of the brain across the midline. They are an important component of the brain’s structural connectivity, allowing for communication and coordination between the two hemispheres of the brain. The major commissural pathways include the corpus callosum, the anterior commissure, and the posterior commissure.
Association pathways are white matter tracts that connect different areas within the same hemisphere of the brain. They are an important component of the brain’s structural connectivity, allowing for communication and coordination between different regions of the brain. Association pathways can be divided into two main types: long association pathways, which connect distant regions of the brain, and short association pathways, which connect adjacent areas.
Projection pathways are white matter tracts that connect the brain cortex to the spinal cord or subcortical regions. They are an important component of the brain’s structural connectivity, allowing for communication between the brain cortex and the rest of the nervous system. Projection pathways can be divided into two main types: sensory projection pathways, which transmit sensory information from the body to the brain, and motor projection pathways, which transmit motor commands from the brain to the body.
Before practicum on Friday, please complete the following:
White Matter Anatomy
-
Reading: a review on recent known and unknown white matter pathways: Bullock DN, Hayday EA, Grier MD, Tang W, Pestilli F, Heilbronner S. A taxonomy of the brain’s white matter: Twenty-one major tracts for the twenty-first century.
During practicum on Friday:
Review of the assignment 1 (10 min)
Introduction to white matter pathways (20 min)

source: Neuroimage. 2021 Dec 15;245:118651.
- Download and open HCP1065 Group-average template 1mm [download] (details) in Step T3
- Download and open tractography atlas [download] (details)
- simplified atlas and labels
- White matter pathways can be categorized into commissural, association, and projection pathways.
- Commissural pathways: pathways connecting left and right hemisphere
- anterior commissure
- corpus callosum
- Association pathways: pathways connecting cortical regions to cortical regions
- arcuate fasciculus (AF), frontal aslant (FAT), superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF) II, III
- cingulum (frontal parahippocampal, frontal parietal, parahippocampal parietal, parahippocampal, and parolfactory), superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF) I
- inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (IFOF), uncinate fasciculus (UF)
- inferior longitudinal fasciculus (ILF), middle longitudinal fasciculus (MdLF), vertical occipital fasciculus (VOF), temporo-parietal aslant tract, extreme capsule.
- Commissural pathways: pathways connecting left and right hemisphere
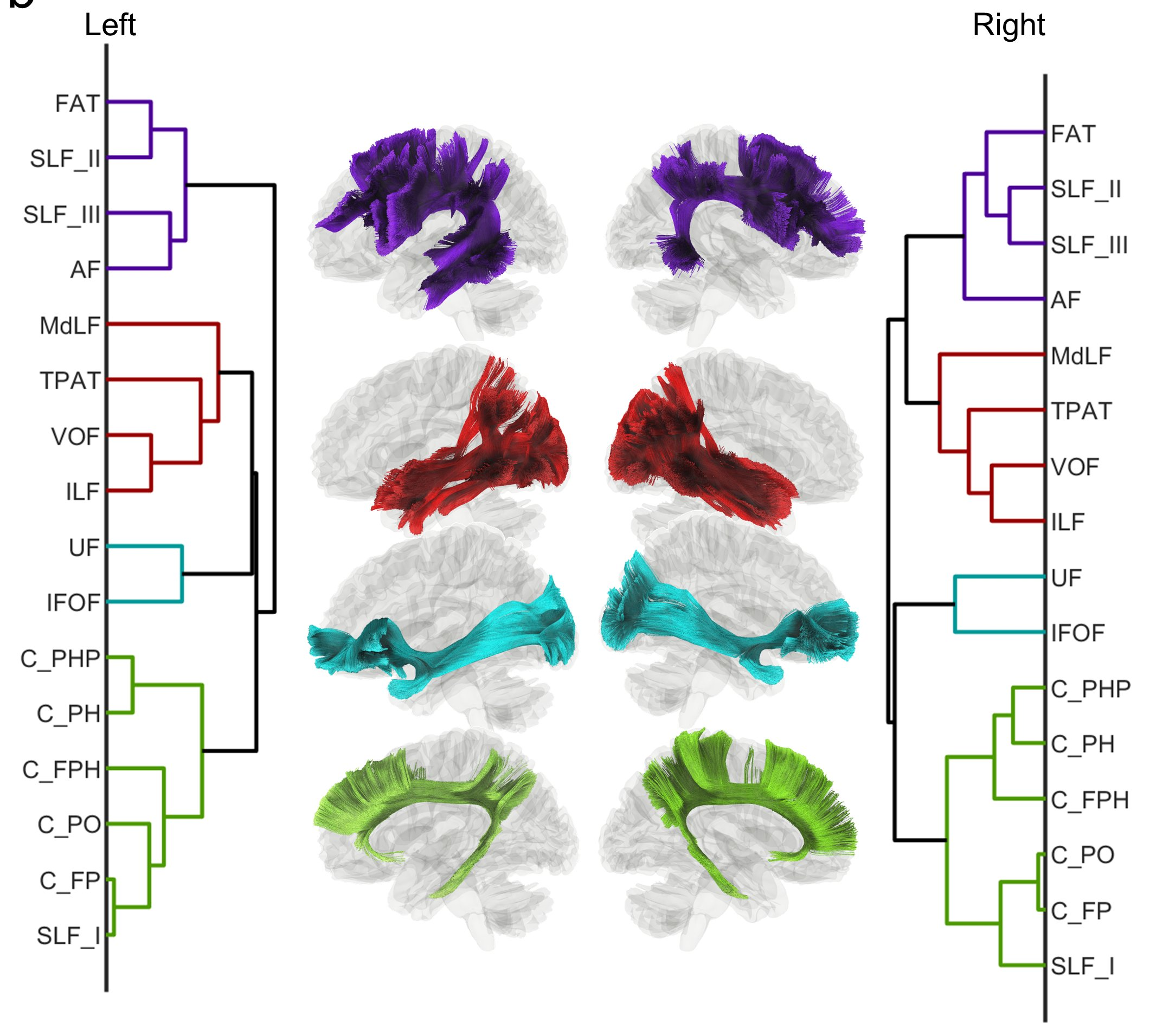
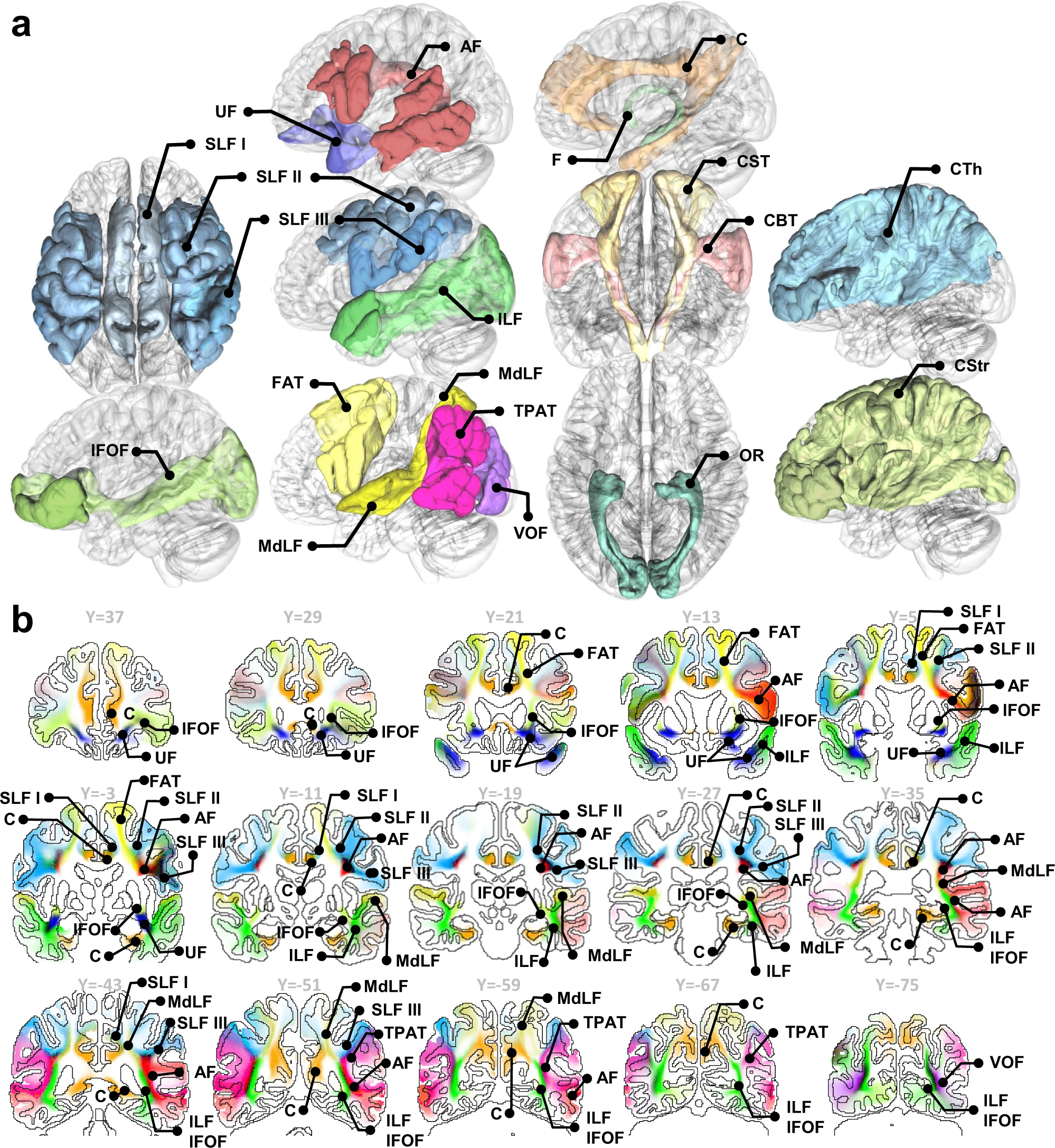
source: Nature communications. 2022 Aug 22;13(1):1-3.
- Projection pathways: pathways connecting cortical regions to the basal ganglia or brain stem nuclei
- thalamus: thalamic radiation (anterior, posterior and superior), acoustic radiation, optic radiation, dentatorubrothalamic tract (DRTT), medial lemniscus
- striatum: corticostriatal tract (anterior, superior, and posterior), fornix
- brain stem nuclei: corticospinal tract, reticulospinal tract, corticobulbar tract, corticopontine tract (frontal, parietal, and occipital),
-
Cerebellum pathways, brainstem pathways, cranial nerves
- White matter regions (not pathways)
- internal capsule
- corona radiata
- centrum semiovale
Virtual dissection (20 min)
- Tract menu
- Tract editing and shortcuts
- Virtual dissection [document]
- Difficulty level (easy): commissural pathways
- Difficulty level (medium): association pathways
- Difficulty level (hard): projection pathways
- Region-based filtering
Automatic Fiber Tracking (10 min)
- Automatic fiber tracking [document]
Assignment: Download FIB file
-
Download 100206.src.gz.gqi.1.7.fib.gz and 100206_T1w.nii.gz
-
Open the FIB file using [Step T3 Fiber Tracking] and click on [Step T3d Tracts][Fiber Tracking] to generate whole brain tracts.
- [Optional] check out document and test different fiber tracking parameters. Observe how changing them leads to different results.
-
Manually segment left arcuate fasciculus, cingulum, uncinate fasciculus, corticospinal tract from whole brain tracks. Compare it with automatic tracking results.
-
Segment left arcuate fasciculus into the acoustic, visual, and lexical encoding part and assign different colors (reference: Giampiccolo D, Duffau H. Controversy over the temporal cortical terminations of the left arcuate fasciculus: a reappraisal. Brain. 2022 Feb 10.)

(Giampiccolo et al. 2022)
 (Segmented on HCP1065 tractography atlas)
(Segmented on HCP1065 tractography atlas)